
SCIENTIFIC NAME
Bison bison
DESCRIPTION
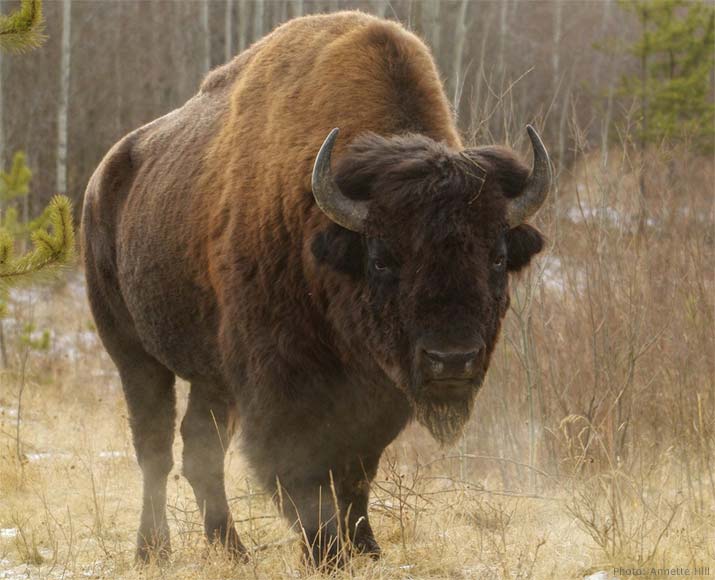
The North American bison, or buffalo, is the largest land animal in North America. A bull can stand 2 m high and weigh more than a tonne. Female bison are smaller than males. A bison has curved black horns on the sides of its head, a high hump at the shoulders, a short tail with a tassel, and dense shaggy dark brown and black hair around the head and neck. Another distinctive feature of the buffalo is its beard.
RANGE
Today, there are comparatively few plains bison. A herd of about 600 is fenced in at Elk Island National Park, 64 km east of Edmonton. There are small numbers at Prince Albert National Park in Saskatchewan, Riding Mountain National Park in Manitoba, and Waterton Lakes National Park in Alberta. There are at least 25 herds of plains bison in national and state parks and wildlife refuges in the United States, numbering more than 10 000 animals. There are more than 140 000 in private collections and on a large number of commercial ranches in both Canada and the United States. The wood bison has always lived to the north of its prairie cousin. In historic times its range was centred in northern Alberta and the adjacent parts of British Columbia, the Northwest Territories, and Saskatchewan. Herds made use of aspen parkland, the eastern slopes of the Rocky Mountains, the lowlands of the Peace and Slave rivers, and the coniferous forests and wetland meadows of the upper Mackenzie Valley. The wood bison was never as abundant as the plains bison, probably numbering no more than 170 000 at its peak.
HABITAT
Historically, bison were known to make movements of up to hundreds of kilometres to take advantage of the changing availability of food plants in different seasons. These movements were most pronounced on the Great Plains, where large herds moved long distances along traditional routes. In contrast, the wood bison in the Mackenzie Bison Sanctuary in the Northwest Territories make only local movements during the year, moving between open meadows and the surrounding forest, in patterns established through traditional use. Most bison live in mixed herds of cows, calves, yearlings, subadults, and a few bulls. The other bulls form groups of their own.
DIET
The grazing habits of bison are similar to those of domestic cattle. Bison eat grasses, sedges, and other ground-growing plants. In the days of free-roaming herds, the plains bison fed on a variety of native grasses, which had great nutritional value. In northern areas, the wood bison fed on a wide variety of grasses and wild forages, but mainly on meadow sedge, an abundant lowland forage, or food suitable for livestock. In winter, they would also eat the tender twigs of scrubland bushes.
BEHAVIOUR
undefinedPRIMARY ECOSYSTEM ROLES
Learn More






